Tourists Witness Uncontacted Amazon Tribe in Peru
posted on February 3rd, 2012 in Amazon Jungle, Indigenous Rights, Peru, Recent Discoveries, Uncontacted Tribes
Peru Struggles To Keep Outsiders Away From Uncontacted Amazon Tribe
Mashco-Piro Indians have been spotted on the banks of a river popular with tourists after increasing logging in the area
Jan 31, 2012
guardian.co.uk
Peruvian authorities say they are struggling to keep outsiders away from a clan of previously isolated Amazon Indians who began appearing on the banks of a jungle river popular with environmental tourists last year.
The behavior of the small group of Mashco-Piro Indians has puzzled scientists, who say it may be related to the encroachment of loggers and low-flying aircraft from nearby natural gas and oil exploration in the south-eastern region of the country.
Clan members have been blamed for two bow-and-arrow attacks on people near the riverbank in Madre de Dios state where officials say they were first seen last May.
One attack badly wounded a forest ranger in October. The following month, another fatally pierced the heart of a local Matsiguenka Indian, Nicolas “Shaco” Flores, who had long maintained a relationship with the Mashco-Piro.
The advocacy group Survival International released photos on Tuesday showing clan members on the riverbank, describing the pictures as the “most detailed sightings of uncontacted Indians ever recorded on camera”.
The British-based group provided the photos exactly a year after releasing aerial photos from Brazil of another tribe classified as uncontacted, one of about 100 such groups it says exist around the world.
(Above: a group of tourists filmed this footage of the Mashco Piro shooting an arrow at them on the Manu River, Peru)
One of the Mashco-Piro photos was taken by a birdwatcher in August, Survival International said. The other two were shot by the Spanish archaeologist Diego Cortijo on 16 November, six days before Flores was killed.
Cortijo, a member of the Spanish Geographical Society, was visiting Flores while on an expedition in search of petroglyphs and said clan members appeared across the river from Flores’s house, calling for him by name.
Flores could communicate with the Mashco-Piro because he spoke two related dialects, said Cortijo, who added that Flores had previously provided clan members with machetes and cooking pots.
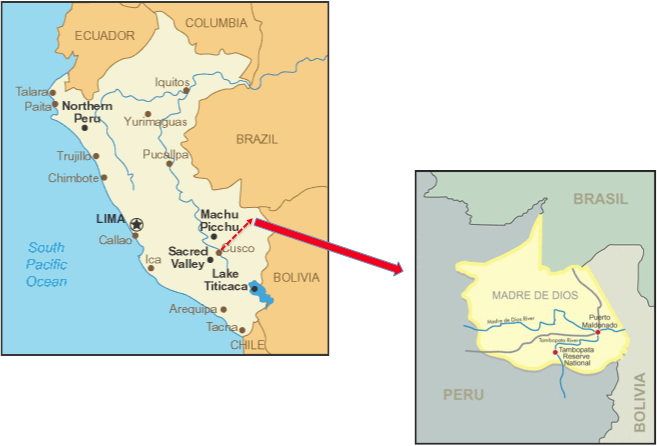
The Mashco-Piro tribe is believed to number in the hundreds and lives in the Manu national park that borders Diamante, a community of more than 200 people where Flores lived.
Although it is not known what provoked the Mashco-Piro clan to leave the relative safety of their tribe’s jungle home, Beatriz Huerta, an anthropologist who works with Peru’s Indepa agency for indigenous affairs, speculated that their habitat was becoming increasingly less isolated.
The upper Madre de Dios region where the tribe lives has been affected by logging, she said. “They are removing wood very close.”
Meanwhile, Huerta said, naturalists in the area and Manu national park officials told her during a recent visit that a rise in air traffic related to natural gas and oil exploration in the region was adversely affecting native hunting grounds, forcing increasing migration by nomadic tribes.
The clan that showed up at the river is believed to number about 60, including some 25 adults, said Carlos Soria, a professor at Lima’s Catholic University who ran Peru’s park protection agency last year.
“It seemed like they wanted to draw a bit of attention, which is a bit strange because I know that on other occasions they had attacked people,” Cortijo said by phone from Spain. “It seemed they didn’t want us to go near them, but I also know that the only thing that they wanted was machetes and cooking pots.”
Cortijo said the group lingered by the river a few minutes, apparently to see if a boat would pass by so they could ask for some tools, something authorities say they have done in the past.
“The place where they are seen is one of heavy transit” of river cargo and tourist passage, and so the potential for more violent encounters remains high, Soria said.
That is compounded by a culture clash. The Mashco-Piro live by their own social code, which Soria said includes the practice of kidnapping women and children from other tribes.
He said the Mashco-Piro were one of about 15 “uncontacted” tribes in Peru that together are estimated to number between 12,000 and 15,000 people living in jungles east of the Andes.
“The situation is incredibly delicate,” said Huerta.
“It’s very clear that they don’t want people there,” she said, noting that they had ransacked a jungle ranger’s post that authorities later removed.
One of the clan’s likely fears is being decimated by disease borne by outsiders, as has occurred with other uncontacted peoples, Huerta said.
After the first sightings, and after tourists left clothing for the Mashco-Piro, state authorities issued a directive in August barring all boats from going ashore in the area. But enforcing it has been difficult as there are few trained and willing local officials.
In response to the Flores killing, authorities sent a team into Diamante to explain to inhabitants that it would be wrong to try to retaliate.
Cortijo said Flores’s death made reaching any understanding with the Mashco-Piro very complicated.
“The problem is that Shaco was the only person who could talk to them,” he said. “Now that he’s dead it’s impossible to make contact.”
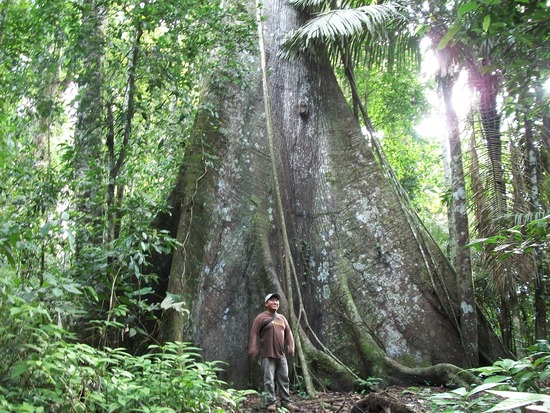
Below: An emergent rainforest tree in Manu National Park, Peru